The Chemistry of Coffee: What Are You Actually Drinking?
Go beyond the caffeine. Coffee is a complex brew of over a thousand chemical compounds. We're breaking down the science of what's in your cup, from powerful antioxidants to the molecules that create its incredible aroma and flavor, and what it all means for your health.
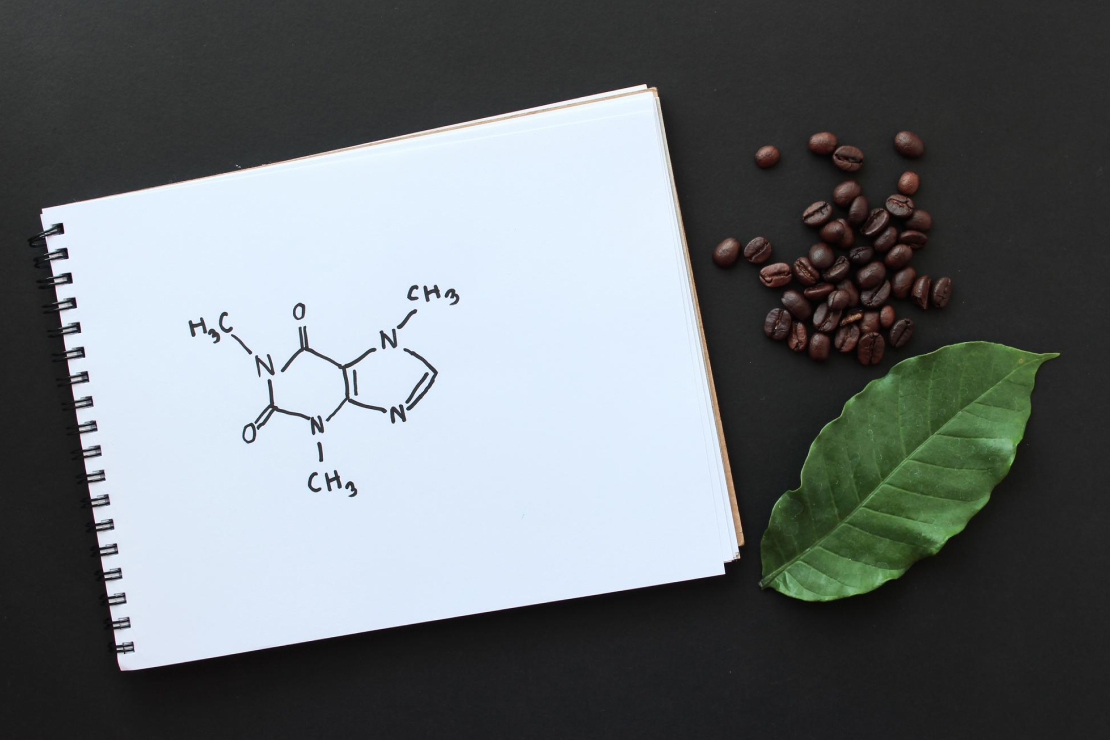
Table of Content
When you take a sip of coffee, you're tasting a complex chemical symphony. While caffeine gets all the attention, it's just one of over 1,000 bioactive compounds that make up this remarkable beverage. These molecules are responsible for its alluring aroma, its rich flavor profile, and its wide-ranging effects on your body and mind.
Understanding the chemistry of coffee can transform your appreciation for it, turning a simple morning habit into a fascinating journey of science. It also helps you make more informed choices about the type of coffee you drink and how you brew it. Let's pull back the curtain and explore the amazing chemical world inside your cup.
Caffeine: The Star of the Show
Let's start with the most famous compound. Caffeine is a natural stimulant that belongs to the methylxanthine class. Its primary superpower is its ability to mimic adenosine, a neurotransmitter that signals sleepiness to the brain. By blocking adenosine receptors, caffeine prevents you from feeling tired and increases neural firing, leading to enhanced alertness, focus, and concentration.
But it doesn't stop there. This increased brain activity stimulates the pituitary gland to release hormones that, in turn, cause the adrenal glands to produce adrenaline. This is the "fight-or-flight" hormone that gives you that familiar coffee jolt, increasing your heart rate and delivering more oxygen to your muscles.
Antioxidants: The Unsung Heroes
Coffee is one of the single largest sources of antioxidants in the Western diet. These compounds are crucial for protecting your body against damage from free radicals, which are unstable molecules that contribute to aging and chronic diseases. The main antioxidant players in coffee are:
- Chlorogenic Acids (CGAs): These are the most abundant antioxidants in coffee. Research suggests they play a role in regulating blood sugar by slowing down carbohydrate absorption in the digestive tract. They may also have anti-inflammatory and blood-pressure-lowering effects. The roasting process can reduce CGA levels, so lighter roasts tend to have a higher concentration.
- Melanoidins: Formed during the roasting process through the Maillard reaction (the same reaction that browns toast), these compounds give coffee its brown color. While less studied than CGAs, melanoidins also exhibit significant antioxidant activity and may contribute to gut health by acting as a prebiotic fiber.
Flavor and Aroma: A Chemist's Delight
That incredible coffee smell? It's the result of hundreds of volatile aromatic compounds working in concert. The roasting process is critical here, as it transforms the chemical precursors in green coffee beans into the complex aromas we love. Key compounds include:
- Pyrazines: These compounds create the toasty, nutty, and roasted aromas.
- Furans: Contribute to the sweet, caramel-like notes in a brew.
- Aldehydes: Responsible for the fruity and floral notes that you might find in specialty coffees.
The taste itself is a balance of bitterness (from compounds like quinine), acidity (from quinic acid and other organic acids), and sweetness (from the caramelization of sugars during roasting).
Diterpenes: A Brewing Method-Dependent Story
Two other important compounds in coffee are the diterpenes known as cafestol and kahweol. These are found in the oily fraction of coffee. Studies have shown that these compounds can raise LDL ("bad") cholesterol levels.
However, their impact is almost entirely dependent on your brewing method. A paper filter is incredibly effective at trapping these oily compounds. Therefore, drinking filtered coffee (like from a standard drip machine, pour-over, or AeroPress) results in a beverage with negligible levels of cafestol and kahweol.
On the other hand, unfiltered brewing methods like French press, Turkish coffee, or Scandinavian boiled coffee leave these compounds in the final cup. While this may be a concern for individuals with high cholesterol, for most people, moderate consumption of unfiltered coffee is generally considered safe and may even have other protective benefits.
Tracking Your Brew with Macro Tracking AI
Understanding the chemistry is fascinating, but what about the practical side? The nutritional profile of your coffee can change dramatically based on what you add to it. A simple black coffee is a chemical wonderland with almost no calories. A creamy, sugary latte is a different story.
Using Macro Tracking AI helps you stay aware of these additions. You can quickly log milk, sugar, or cream to see how they fit into your daily macro goals. For complex café drinks, the AI camera scan provides an easy way to get a nutritional estimate, turning a chemical question mark into clear, actionable data. It ensures you can enjoy the complex chemistry of coffee without unknowingly consuming excess calories or sugar.
Conclusion: More Than Just a Bean
Your daily cup of coffee is a miniature chemistry lab, a complex interaction of hundreds of compounds that give it its unique character and effects. From the stimulating power of caffeine to the protective benefits of antioxidants, it's a beverage that has a profound impact on our biology.
By understanding what you're actually drinking, you can make smarter choices—whether that's opting for a lighter roast to maximize antioxidants or using a paper filter to reduce diterpenes. This knowledge deepens your appreciation and empowers you to make your coffee ritual a truly beneficial part of your healthy lifestyle.
Start Your Health Journey Today
Download Macro Tracking AI and take control of your nutrition with the power of artificial intelligence.
Download on App Store

